In this article, we’ll explore various types of motors each with its unique characteristics and applications while providing vivid images that bring each concept to life. Learning the different types of motors names in English is a good thing for mechanics and workers .From the reliable AC motor that hums quietly in your refrigerator to the powerful DC motor driving electric vehicles, each type plays a crucial role in its respective domain. Join us as we embark on this enlightening journey through the world of motors, where names like stepper, servo, and induction take center stage alongside their captivating visuals.
List of Types of Motors Names in English
- DC Motor
- AC Motor
- Synchronous Motor
- Asynchronous Motor
- Stepper Motor
- Servo Motor
- Induction Motor
- Brushed DC Motor
- Brushless DC Motor
- Universal Motor
- Linear Motor
- Gear Motor
- Shaded Pole Motor
- Reluctance Motor
- Permanent Magnet Motor
- Hysteresis Motor
- Split Phase Motor
- Compound DC Motor
- Series DC Motor
- Parallel DC Motor
Types of Motors Names and Pictures in English
- DC Motor
A motor powered by direct current electricity.
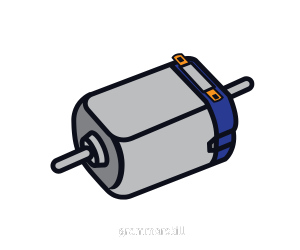
- Synchronous Motor
a type of motor that keeps a consistent speed by synchronizing with the frequency of its power supply.
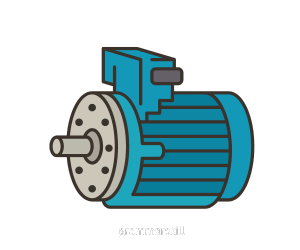
- Stepper Motor
A motor that moves in precise increments, ideal for achieving accurate placement.

- Servo Motor
This type of motor is utilized in control systems to achieve accurate motion, frequently employed in robotic applications.

- Induction Motor
A type of motor that produces torque through an electric current generated by an electromagnetic field.

- Brushed DC Motor
This is a basic direct current motor that employs brushes to supply electrical current to the rotor.

- Linear Motor
A type of motor that generates linear motion rather than spinning movement.

- Gear Motor
A motor combined with a gearing mechanism to lower speed while increasing torque.
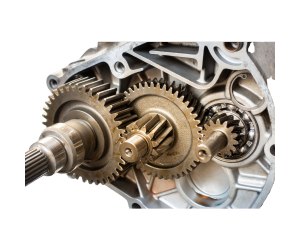
- Shaded Pole Motor
A simple, energy-efficient motor commonly found in small devices and fans.

- Reluctance Motor
a motor that operates using the reluctance force generated by a magnetic field.

- Permanent Magnet Motor
A type of motor that generates its magnetic field for movement through the use of permanent magnets.
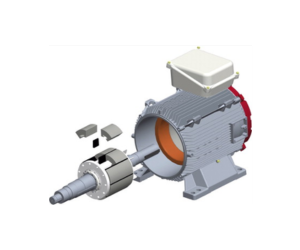
- Split Phase Motor
A self-starting motor featuring dual windings, commonly utilized in compact machinery.

- Series DC Motor
A series-connected high torque motor features its armature and field windings linked together.

60 Motors Names in English
- Slip Ring Motor
- Single-phase Induction Motor
- Three-phase Induction Motor
- Squirrel Cage Motor
- Capacitor Start Motor
- Capacitor Run Motor
- Permanent Split Capacitor Motor
- Double Cage Motor
- Wound Rotor Motor
- Variable Reluctance Motor
- Switched Reluctance Motor
- Universal Synchronous Motor
- Universal Asynchronous Motor
- Hysteresis Synchronous Motor
- Universal AC Motor
- Traction Motor
- High Voltage Motor
- Low Voltage Motor
- Explosion-proof Motor
Types of Motors Names and Pictures
- Slip Ring Motor
A type of motor known as an induction motor features external resistors linked to the rotor windings via slip rings.

- Single-phase Induction Motor
A single-phase electric motor, commonly utilized in home appliances, is a type of AC motor.

- Three-phase Induction Motor
A highly effective motor operating on three-phase power, frequently utilized in industrial equipment.

- Squirrel Cage Motor
A durable variety of induction motor featuring a rotor designed in the form of a squirrel cage.

- Capacitor Start Motor
a robust rotor induction motor designed in the shape of a squirrel cage.

- Capacitor Run Motor
A motor that uses a capacitor in the running circuit to enhance performance.

- Permanent Split Capacitor Motor
A type of motor that incorporates a capacitor within its operating circuit to improve efficiency.

- Double Cage Motor
A dual-cage motor features one rotor designed to provide initial torque and another optimized for operational efficiency.
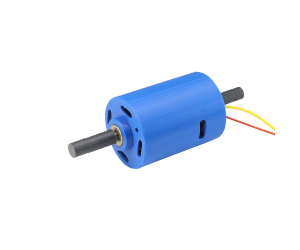
- Wound Rotor Motor
A wound rotor induction motor linked to external resistors for enhanced speed regulation.

- Variable Reluctance Motor
A type of motor that functions by adjusting the reluctance within its magnetic circuit.

- Switched Reluctance Motor
A motor featuring a straightforward design operates by altering the magnetic field within the stator.

- Universal Synchronous Motor
A motor capable of operating on both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) while maintaining synchronous speed.

- Universal Asynchronous Motor
A type of motor capable of operating at various speeds and utilizing both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) power sources.

- Universal AC Motor
High-speed AC motors are commonly found in various household appliances.

- Traction Motor
A type of motor specifically engineered to power transportation systems such as electric trains or trams.

- Low Voltage Motor
A type of motor specifically engineered for operation at reduced voltage levels, commonly found in compact machinery.

- Explosion-proof Motor
A motor engineered to eliminate the risk of sparks or excessive heat in dangerous settings.

List of Motors Names in English
- Submersible Motor
- Hydraulic Motor
- Electric Vehicle Motor
- Pneumatic Motor
- Torque Motor
- Claw Pole Motor
- Disk Motor
- Coreless Motor
- Outer Rotor Motor
- Inrunner Motor
- Outrunner Motor
- Slotless Motor
- Ironless Motor
- Eddy Current Motor
- Direct Drive Motor
- Hybrid Stepper Motor
- Micro Motor
- Hollow Shaft Motor
- Frameless Motor
Different types of Motors Names and Pictures
- Submersible Motor
An underwater motor specifically engineered for operation, frequently utilized in pumping systems.

- Hydraulic Motor
A motor that operates using pressurized fluid, commonly utilized in heavy machinery.

- Electric Vehicle Motor
a specialized engine designed specifically to power electric cars.

- Pneumatic Motor
A commonly used type of motor in various tools is the air motor, which operates using compressed air.

- Torque Motor
a motor designed for precise control capable of generating significant torque at low rotational speeds.

- Claw Pole Motor
A motor featuring magnetic poles designed like claws to optimize power transmission.
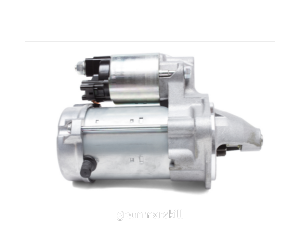
- Disk Motor
A compact and highly efficient motor featuring a rotor that is shaped like a flat disk.
- Coreless Motor
A lightweight motor without an iron core, providing high efficiency and fast response.

- Outer Rotor Motor
A motor where the rotor spins outside the stator for better torque.

- Inrunner Motor
A motor featuring a spinning inner rotor that provides elevated speeds.

- Slotless Motor
A motor designed with a slotless stator, which decreases noise levels and enhances efficiency.
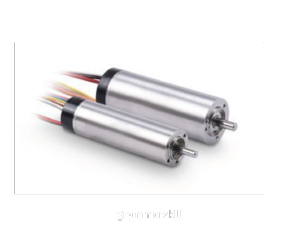
- Ironless Motor
A rotor made without iron, which decreases weight and enhances response time in the motor.
- Eddy Current Motor
A motor that employs eddy currents in its rotor to ensure seamless functionality.
- Direct Drive Motor
A motor that powers a machine directly, eliminating the requirement for gears or belts.

- Micro Motor
A miniature motor located in small devices like medical instruments and watches.
- Frameless Motor
A motor designed without an external casing, enabling tailored integration into various devices.

- Hover Motor
A device designed to generate upward force, commonly used in aircraft or hovercraft.
FAQs
- What are the four main types of motors?
The four main types of motors are DC motors, AC motors, stepper motors, and servo motors. Each type has its own unique characteristics and applications.
- What are the types of AC and DC motors?
There are two main types: AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) motors. Each type has its own subcategories that cater to different applications. For AC motors, the most common types are induction motors and synchronous motors. Induction motors are widely used in household appliances and industrial machines because they’re robust and easy to maintain. Synchronous motors, on the other hand, run at a constant speed and are often found in applications requiring precise control.
- How are motors classified?
Motors are primarily classified based on their power source and operational principles. The two main categories are AC (alternating current) motors and DC (direct current) motors. AC motors are further divided into synchronous and asynchronous (or induction) motors, while DC motors can be classified into brushed and brushless types. Each type has its own advantages and is suited for different applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery.
Conclusions
In summary, understanding the different types of motors is essential for anyone looking to dive into the world of engineering or electronics. From electric and stepper motors to more specialized options like servo and brushless motors, each type serves its unique purpose and application. Knowing these distinctions can help you make informed decisions whether you’re building a simple project or designing complex machinery. As technology continues to evolve, staying updated on motor advancements will only enhance your skills and knowledge. So, explore these motor types further, and see how they can power your next creative endeavor.
