Modal verbs are an essential part of English grammar, serving as auxiliary verbs that express necessity, possibility, ability, or permission. They help convey the attitude of the speaker towards the action being discussed. Common modal verbs include can, could, may, might, must, and shall. When someone says, “I can swim,” they indicate their ability to do so; conversely, if they say, “I may go to the party,” it expresses a possibility rather than certainty. Understanding how to use these verbs effectively is crucial for mastering English grammar and enhancing communication skills.
What Are Modal Verbs?
Modal verbs are a fascinating aspect of English grammar that often goes unnoticed in everyday communication. These auxiliary verbs, which include can, could, may, might, must, and should, serve a unique purpose in conveying necessity, possibility, ability, and permission. For example, when I say “I can swim,” I’m expressing my ability to do something; whereas if I say “You must finish your homework,” I’m indicating an obligation. This subtle yet powerful function of modal verbs adds nuance to our language and enables us to express complex ideas efficiently.
Understanding modal verbs has been pivotal in my journey to mastering English grammar skills.
Types of Modal Verbs and Their Uses
1. Can and Could
- Can: Indicates ability or possibility. It is used for present or general abilities.
- Example: He can play the drum.
- Could: Used for past abilities or polite requests.
- Example: When He was young he run fast.
| Model verb | Use case | Example |
| Can | Ability | She can speak four language. |
| Could | Past Ability | He could drive when was ten. |
May and Might.
- May: Used for formal requests or to express possibility.
- Example: May He leave early today?
- Might: Suggests a lower probability than “may.”
- Example: It might be hot tomorrow.
| Model verb | Use case | Example |
| May | Permission | I may not go to the party. |
| Might | Possibility (Less certain) | It might rain today. |
Shall and Should
- Shall: Traditionally used with “I” and “we” for future actions or suggestions.
- Example: Shall we eat dinner.
- Should: Expresses advice, obligation, or expectation.
- Example: You should iron your clothes early.
| Modal verb | Use case | Example |
| Shall | Suggestion | Shall we go to the market? |
| Should | Advice | You should complete your project today. |
Will and Would
- Will: Indicates future actions or strong intentions.
- Example: He will call you tomorrow.
- Would: Used for polite requests or hypothetical situations.
- Example: Would you like some coffee.
| Model verb | Use case | Example |
| Will | Future Intentions | I will buy a new bag. |
| Would | Polite Requests | Would you please do the house chores for me? |
. Must and Ought to.
- Must: Indicates necessity or strong obligation.
- Example: You must wear an apron while cooking.
- Ought to: Used to express moral obligation or advice.
- Example: You ought to thanx your uncle for the gift.
| Model verb | Use Case | Example |
| Must | Necessity/Obligation | You must stich your dress till tomorrow. |
| Ought | Moral Obligation/Advice | We ought to help Palestinians kids. |
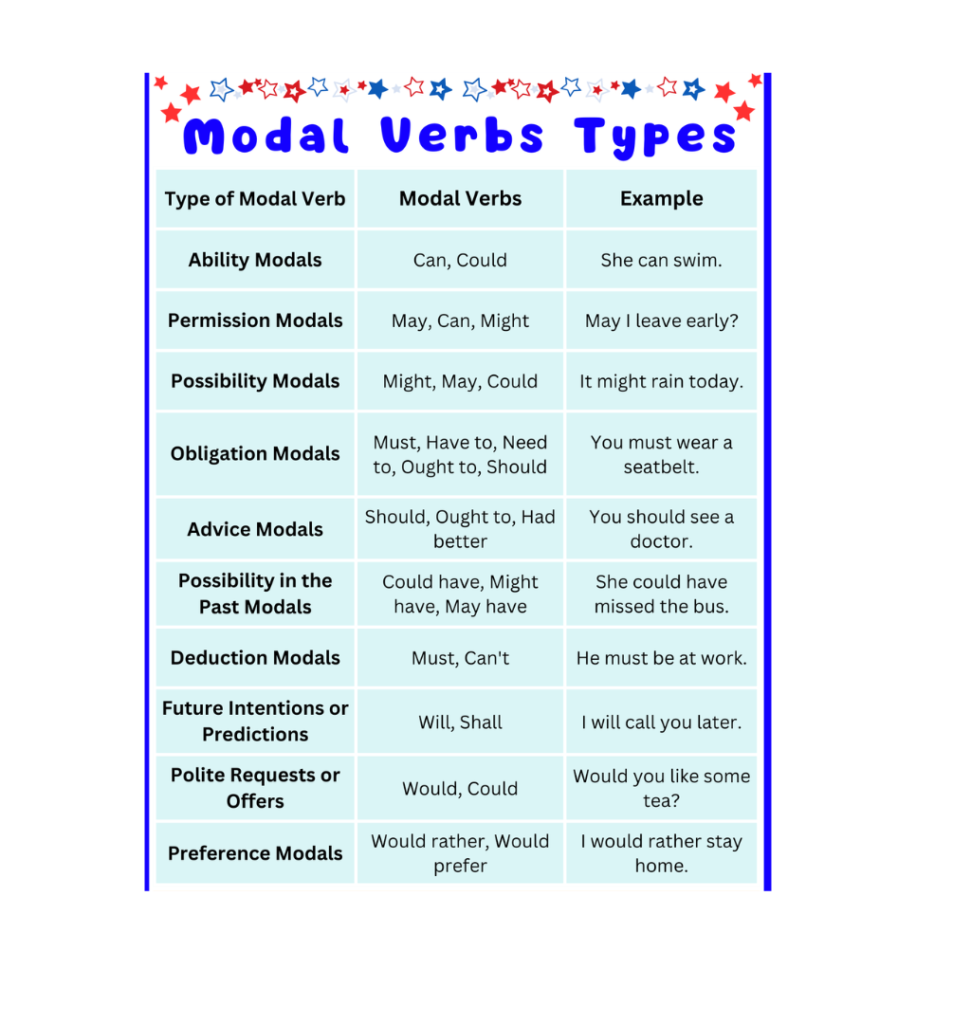
Advanced Usage of Modal Verbs.
Modal verbs can also be used in various advanced structures to convey nuanced meanings. Here are some examples:
Modal Verbs in Conditional Sentences
Modal verbs are commonly used in conditional sentences to show possibilities, suggestions, or imaginary situations. Here are some examples:
- Could: If I could speak English, I would move to America.
- Might: If it rains, we might stay in home.
- Would: If he work harder, he would win the match.
Modal Verbs in Questions.
Modal verbs can be used to form questions, which often involve asking for permission or making polite requests. Here are some examples:
- Can: Can I borrow your book?
- May: May I sit with you?
- Would: I would appreciate your assistance.
Modal Perfect
Perfect modals go further and allow us to express those thoughts/feelings about the past. Here are some examples:
- Must have: He must have done his homework.
- Could have: She could have washed her dress.
- Might have: They might have arrived at the station.
| Modal verb | Advance use case | Example |
| Would | Hypothetical situation | If you would have study harder you would be successful. |
| Must | Speculation about past | She must have been exhausted. |
List of Modal Verbs.
- Can
- Could
- May
- Might
- Shall
- Should
- Will
- Would
- Must
- Ought to
- Need to
- Have to
- Have better
- Would rather
- Could have
- Might have
- Should have
- Would have
- Will have
- Must have
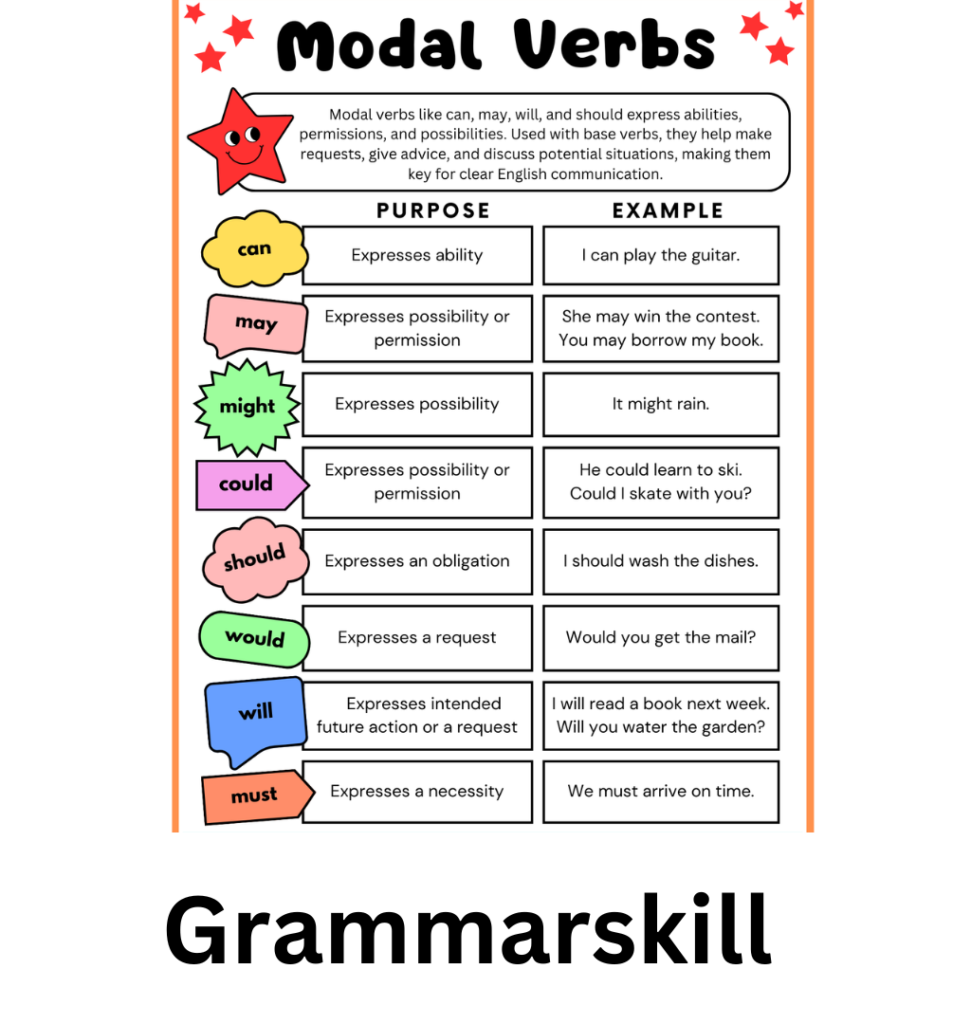
Modal Verbs Example Sentences
- He Can dance very well.
- You MUST pack your bag before dinner.
- I Might come to school tomorrow.
- You Should not go to Ali’s house.
- She Could play the piano when she was in school.
- May I use your pencil?
- You Ought to thanx your uncle for the gift.
- He Will write an essay.
- You Need to help the poor to erase your sins.
- I Would like a cup of coffee.
- HE Has to take care of the baby.
- He Might not forgot the instruction.
- He Should not eat peanuts because he is allergic to them.
- CAN you please clean the room?
- She Must not play in the dirt.
- You Don’t have your keys.
- He Wouldn’t play cricket in rain.
- Shall we go for lunch today.
- You Had better not argued with him.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Using the wrong modal verb: Always consider the context and meaning.
- Incorrect: He can be at home now. (Wrong because “can” suggests ability, not certainty)
Correct: He might be at home now. (Correct as it indicates possibility)
Forgetting the base form of the main verb: Remember, modal verbs are followed by the base form of the verb.
- Incorrect: She can to swim.
- Correct: She can swim.
For more Grammar knowledge stay connected with Grammar Skills.
FAQs
What are modal verbs and examples?
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that express necessity, possibility, permission, ability, or obligation.
What are modal verbs Basic 5?
The Basic 5 modal verbs include can, could, may, might, and must.
What is a modal verb example for kids?
A great example for kids is the verb can. When you say, I can swim, it shows that you have the ability to swim. It’s a simple way to explain how modal verbs help us communicate what we are capable of doing.
Have to modal verb examples?
Some common examples include can, could, may, might, must, shall, and should.

One Response